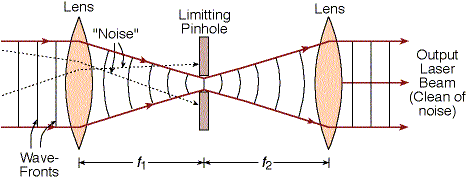

The structure of the spatial filter is of a Kepler’s telescope with a pinhole in the focal point of the two lenses.
The laser beam is focused to a small spot by the first lens, and then pass through a small pinhole.
The pinhole size is 2-3 times the size of the spot diameter at the focus.
Since the “noise” rays is not aligned with the optic axis of the laser beam, they are focused at points not on the optic axis.
Thus, the “noise” rays are not transmitted through the pinhole.
The second lens is used to create again the parallel beam of the laser.
Actually, spatial filter is a Kepler’s beam expander with a pinhole at the focus.