Rami Arieli: "The
Laser Adventure" Chapter 3.2 page 4
Example 3.1: Helium-Neon Laser
Figure 3.4 show the energy level diagram of Helium-Neon laser, with
the possible transitions.
The mass of the Helium atom is about one-fifth of the mass of the Neon
atom.
The amount of Helium in the tube is about 6 times the amount of Neon.
Thus Helium atoms have more chance to receive energy from the accelerated
electrons, and transfer into the excited energy levels E3 and
E5.
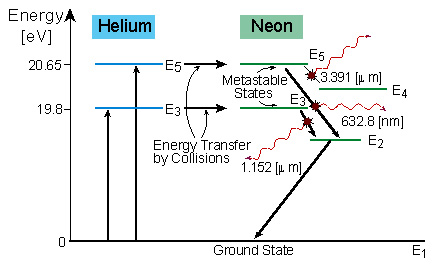 Figure 3.4: Energy Level Diagram of Helium-Neon
Laser
Neon atom have two excited energy levels (E3 and E5)
which are very close to the excited energy levels of the Helium atom. The
excited Helium atoms transfer their excitation energy to the Neon atoms
by collisions - Resonance excitation.
Figure 3.4: Energy Level Diagram of Helium-Neon
Laser
Neon atom have two excited energy levels (E3 and E5)
which are very close to the excited energy levels of the Helium atom. The
excited Helium atoms transfer their excitation energy to the Neon atoms
by collisions - Resonance excitation.
Energy from the He-Ne laser is emitted at wavelengths which correspond
to the energy difference between the levels:
E5 - E4 = > l1
= 3.391 [mm]
E5 - E2 = > l2
= 0.632 [mm]
E3 - E2 = > l3
= 1.152 [mm]
Later we shall understand how to choose the specific required wavelength
at the output of the laser.

