Rami Arieli: " The
Laser Adventure" Chapter 2.1 page 1
2.1 Bohr model
of the atom.
Lasing action
is a process that occurs in matter.
Since matter is composed of atoms, we need to understand (a little)
about the structure of the atom, and its energy states.
We shall start with the semi-classical model, as suggested in
1913 by Niels Bohr,
and called: The Bohr model of the
atom.
According to this model, every atom is composed of a very massive
nucleus with a positive electric
charge (Ze), around it electrons are moving in specific paths.
Z = Number of protons in the nucleus,
e = Elementary charge of the electrons:
e = 1.6*10-19 [Coulomb]
Figure 2.1 illustrates a simple, but adequate, picture
of the atom, the Bohr model:
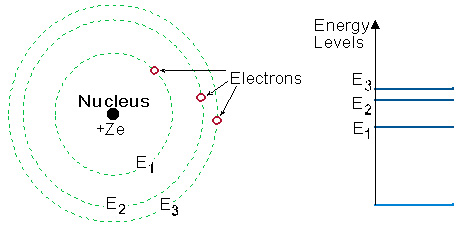
Fig 2-1:Bohr picture of the Atom
Every "allowed orbit" of the electron around
the nucleus, is connected to a specific energy level.
The energy level is higher as the distance of the "orbit" from the
nucleus increases. Since for each atom there are only certain "allowed
orbits", only certain discrete energy levels exist,
and are named: E1, E2, E3,
etc.

